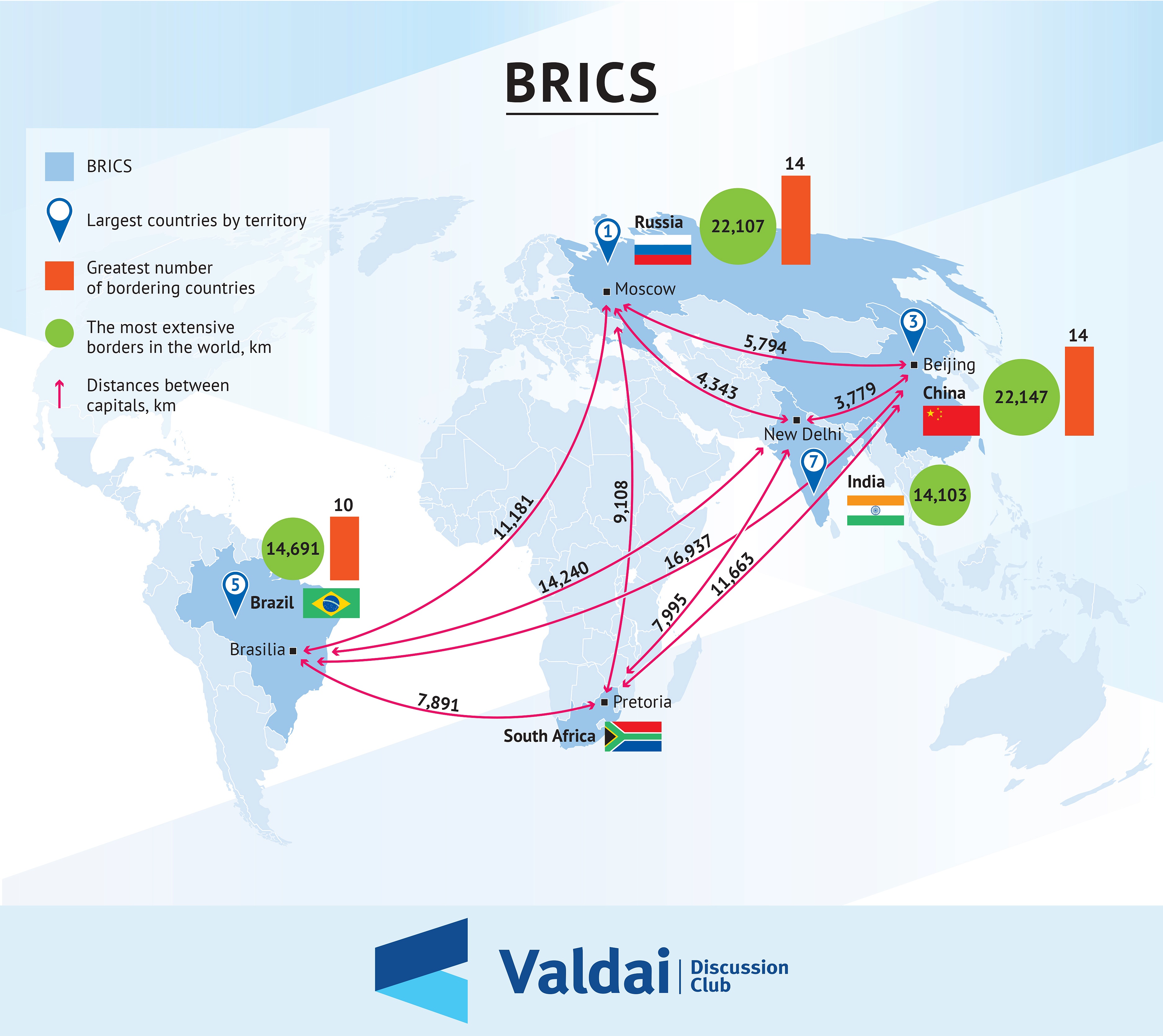
In today’s interconnected world, the term "BRICS" has become a buzzword synonymous with emerging markets and economic growth. Representing Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, this coalition of nations has carved a niche for itself in global economics, politics, and trade. What began as an acronym coined by economist Jim O’Neill in 2001 has evolved into a powerful alliance that challenges traditional economic powerhouses. With over 40% of the world’s population and a combined GDP that rivals that of the G7, the BRICS nations are reshaping the global economic landscape.
These countries are not just economic entities; they are cultural, political, and social powerhouses that influence global policies and decisions. Each member of the BRICS bloc brings unique strengths to the table, from China’s manufacturing prowess to India’s technological advancements and Brazil’s agricultural exports. Together, they are fostering collaboration in areas such as trade, investment, and sustainable development. Their collective voice is increasingly being heard in international forums, where they advocate for reforms in global governance structures like the United Nations and the World Bank.
As we delve deeper into the BRICS alliance, it becomes clear that their significance extends beyond economic metrics. These nations are also working together to address global challenges such as climate change, poverty alleviation, and technological innovation. Their shared vision for a multipolar world order is driving new initiatives, such as the establishment of the New Development Bank (NDB), which aims to fund infrastructure projects in emerging economies. With their combined influence and shared goals, the BRICS countries are poised to redefine the future of global economics and diplomacy.
Read also:Mysteries And Significance Ari Kytysa Erome
Table of Contents
- What Are the Core Objectives of BRICS?
- How Does the BRICS Alliance Influence Global Trade?
- Which BRICS Countries Are Leading in Economic Growth?
- How Is BRICS Shaping the Future of Sustainable Development?
- What Role Does the New Development Bank Play in BRICS?
- Are the BRICS Nations Challenging Global Economic Powerhouses?
- How Does BRICS Promote Cultural and Political Cooperation?
- What Are the Future Prospects for BRICS in a Changing World?
What Are the Core Objectives of BRICS?
The BRICS alliance was formed with the primary goal of fostering economic cooperation among its member nations. This collaboration is not just about trade and investment but also about creating a platform for these emerging economies to have a stronger voice in global affairs. One of the key objectives is to promote sustainable economic growth by leveraging the strengths of each member country. For instance, China’s manufacturing capabilities complement Brazil’s agricultural exports, while India’s technological innovations align with South Africa’s mineral resources.
Another significant objective of BRICS is to reform global governance institutions. The member nations have consistently advocated for a more inclusive and representative international order. They argue that institutions like the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank are dominated by Western countries and fail to adequately represent the interests of emerging economies. By working together, BRICS aims to push for reforms that ensure fairer representation and decision-making power for developing nations.
Furthermore, the alliance seeks to enhance cooperation in areas such as science, technology, and innovation. Joint research initiatives and collaborative projects are encouraged to address global challenges like climate change, energy security, and public health. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, BRICS nations shared resources and expertise to combat the crisis. This spirit of collaboration underscores the alliance’s commitment to not just economic prosperity but also global well-being.
How Does the BRICS Alliance Influence Global Trade?
The BRICS nations collectively account for a significant portion of global trade, and their influence in this domain is growing rapidly. By forming strategic partnerships and trade agreements, these countries are reducing their reliance on traditional Western markets and creating new opportunities for intra-BRICS trade. For example, China and India have signed numerous bilateral agreements that facilitate the exchange of goods and services, while Brazil and Russia have strengthened their trade ties through energy partnerships.
One of the most notable initiatives is the establishment of the BRICS Payment System, which aims to reduce dependency on the US dollar in international transactions. This system promotes the use of local currencies for trade settlements, thereby enhancing financial independence and reducing exposure to currency fluctuations. Such measures are particularly important in a world where geopolitical tensions often disrupt global supply chains.
Key Sectors Driving BRICS Trade
- Energy: Russia and Brazil are major energy exporters, supplying oil, natural gas, and renewable energy solutions to other BRICS nations.
- Technology: India and China are leading the way in technological innovation, with collaborations in artificial intelligence, 5G, and digital infrastructure.
- Agriculture: Brazil’s agricultural exports, including soybeans and beef, play a crucial role in meeting the food security needs of other member countries.
Impact on Global Supply Chains
The BRICS alliance is also reshaping global supply chains by promoting regional integration and self-sufficiency. By investing in infrastructure projects and logistics networks, these nations are creating a more interconnected and resilient trade ecosystem. This is particularly evident in Africa, where South Africa is leveraging its position as a gateway to the continent to facilitate trade with other BRICS members.
Read also:Jelly Rolls Real Name Jason Deford A Deep Dive Into The Life Of A Rising Star
Which BRICS Countries Are Leading in Economic Growth?
Among the BRICS nations, China and India have consistently been the front-runners in terms of economic growth. China’s rapid industrialization and export-oriented policies have made it the world’s second-largest economy, while India’s focus on digital transformation and service sectors has fueled its rise as a global tech hub. Both countries have also made significant strides in poverty alleviation and infrastructure development, setting benchmarks for other emerging economies.
China’s Economic Dominance
China’s economic success is driven by its manufacturing sector, which accounts for a substantial portion of global production. The country is also a leader in renewable energy, with massive investments in solar and wind power. Additionally, China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has strengthened its trade ties with other BRICS nations, particularly through infrastructure projects in Africa and South Asia.
India’s Technological Leap
India, on the other hand, is making waves in the technology sector. With a thriving startup ecosystem and a growing number of unicorns, the country is positioning itself as a global leader in innovation. The government’s "Make in India" initiative has further boosted domestic manufacturing, while policies promoting digital inclusion have expanded internet access to millions of citizens.
Other Notable Performers
Brazil and Russia also contribute significantly to the BRICS economy, albeit in different ways. Brazil’s agricultural exports are a cornerstone of its economy, while Russia’s energy resources make it a key player in global energy markets. South Africa, though smaller in size, plays a vital role in connecting the BRICS bloc to the African continent.
How Is BRICS Shaping the Future of Sustainable Development?
Sustainability is a cornerstone of the BRICS agenda, with member nations committing to various initiatives aimed at addressing climate change and promoting green growth. One of the key areas of focus is renewable energy, where countries like China and India are investing heavily in solar and wind power projects. These efforts are not only reducing carbon emissions but also creating new job opportunities and fostering technological innovation.
The alliance is also working to enhance environmental cooperation through platforms like the BRICS Environment Ministers’ Meeting. These forums provide a space for member countries to share best practices and develop joint strategies for tackling environmental challenges. For instance, Brazil’s expertise in forest conservation is being leveraged to combat deforestation in other regions, while South Africa’s experience in water management is helping address scarcity issues in arid areas.
Green Finance and the New Development Bank
The New Development Bank (NDB), established by BRICS, plays a crucial role in funding sustainable development projects. With a focus on green finance, the NDB has approved loans for renewable energy initiatives, urban infrastructure, and climate resilience programs. This financial support is instrumental in helping member countries transition to low-carbon economies.
What Role Does the New Development Bank Play in BRICS?
The New Development Bank (NDB) is one of the most significant achievements of the BRICS alliance. Established in 2014, the bank aims to provide financial support for infrastructure and sustainable development projects in emerging economies. Unlike traditional financial institutions, the NDB operates on a model of equal representation, with each member country holding an equal share of voting power.
The NDB has already approved billions of dollars in loans for projects ranging from renewable energy to urban transportation. For example, it has funded solar power plants in India, water management systems in Brazil, and healthcare infrastructure in South Africa. These investments are not only improving living standards but also fostering economic growth and resilience.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its successes, the NDB faces challenges such as ensuring transparency and managing geopolitical tensions among member nations. However, its potential to drive sustainable development and reduce dependency on Western financial institutions remains unparalleled. As the bank expands its operations, it is likely to play an even more pivotal role in shaping the future of global finance.
Are the BRICS Nations Challenging Global Economic Powerhouses?
The rise of BRICS has undoubtedly challenged the dominance of traditional economic powerhouses like the United States and the European Union. By advocating for reforms in global governance and promoting alternative financial systems, these nations are creating a multipolar world order. For instance, their push for greater representation in the IMF and World Bank reflects a broader desire to democratize international institutions.
Geopolitical Implications
From a geopolitical perspective, BRICS serves as a counterbalance to Western influence. The alliance’s emphasis on multilateralism and non-interference in domestic affairs resonates with many developing nations, further expanding its reach. This growing influence is evident in forums like the United Nations, where BRICS countries often present a united front on key issues.
Economic Competitiveness
Economically, BRICS nations are increasingly competing with Western powers in areas such as technology, manufacturing, and finance. For example, China’s advancements in 5G technology and India’s leadership in software services are challenging the dominance of Silicon Valley. Similarly, the BRICS Payment System is an alternative to the SWIFT network, offering a more decentralized approach to global finance.
How Does BRICS Promote Cultural and Political Cooperation?
Beyond economics, BRICS is fostering cultural and political cooperation among its member nations. Through initiatives like the BRICS Film Festival and the BRICS Network University, the alliance is promoting cultural exchange and mutual understanding. These programs not only celebrate diversity but also strengthen people-to-people ties, which are essential for long-term collaboration.
Political Dialogue and Diplomacy
Politically, BRICS serves as a platform for dialogue on issues ranging from security to human rights. The annual BRICS Summit brings together leaders from member countries to discuss shared challenges and opportunities. This high-level engagement is complemented by working groups and task forces that address specific issues like counterterrorism and cybersecurity.
Shared Values and Vision
At its core, BRICS is built on shared values such as sovereignty, equality, and mutual respect. These principles guide the alliance’s approach to international relations and ensure that its actions align with the interests of its member nations. By promoting a multipolar world order, BRICS is paving the way for a more inclusive and equitable global system.
What Are the Future Prospects for BRICS in a Changing World?
As the global landscape continues to evolve, the future of BRICS looks promising yet challenging. On one hand, the alliance is well-positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in areas like digital transformation, renewable energy, and regional integration. On the other hand, it must navigate geopolitical tensions, economic uncertainties, and internal disparities to maintain its momentum.
Potential for Expansion
One of the most exciting prospects for BR