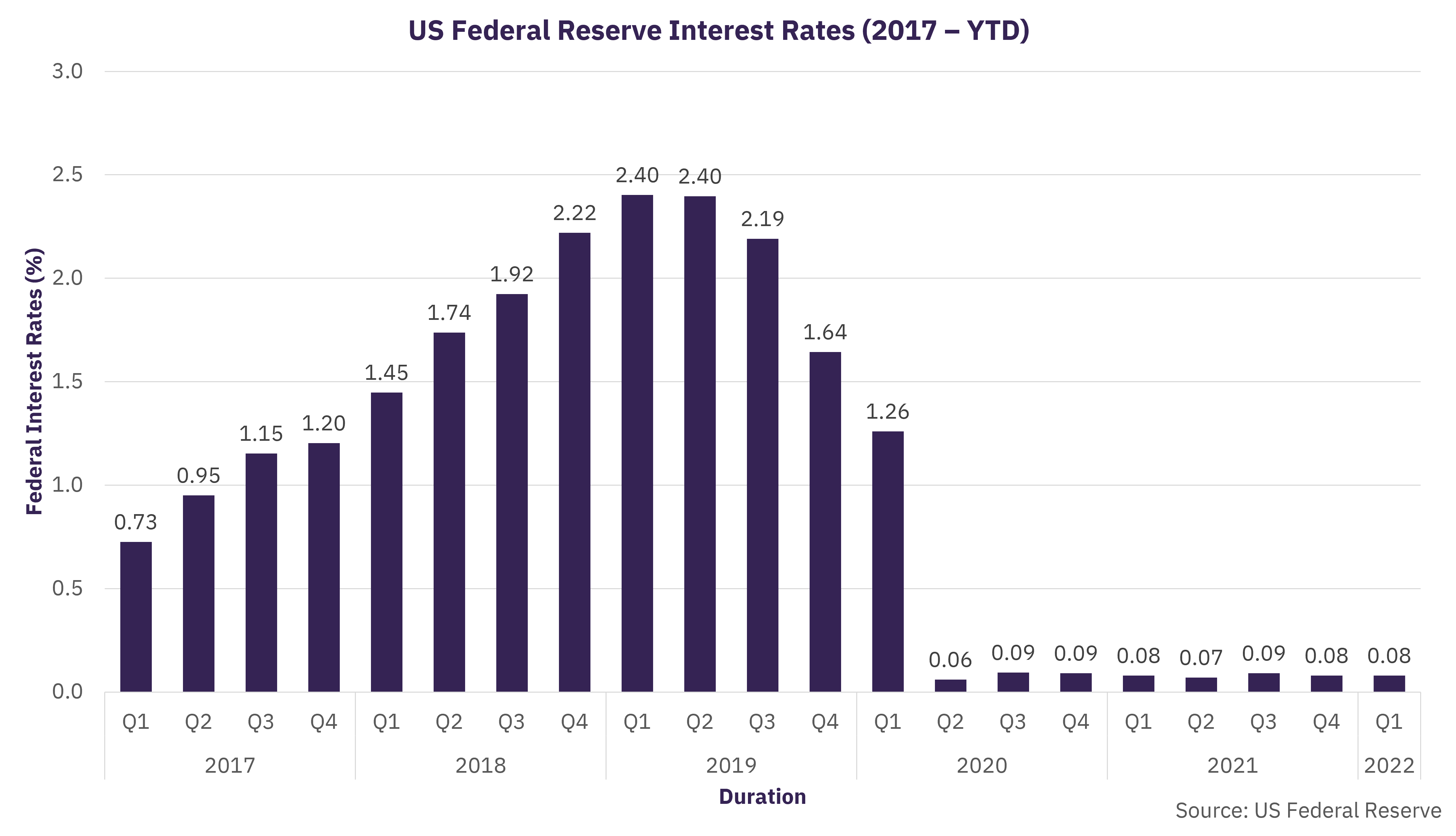
The Fed adjusts these rates to achieve its dual mandate: promoting maximum employment and maintaining stable prices. By raising or lowering interest rates, the central bank can either stimulate economic growth or cool down inflation. This delicate balancing act has profound implications for households, businesses, and global markets alike.
In recent years, the Fed has faced unprecedented challenges, including the economic fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent inflationary pressures. As a result, federal reserve interest rates have fluctuated significantly, reflecting the central bank's efforts to navigate a rapidly changing economic landscape. From near-zero rates during the pandemic to aggressive hikes in 2022 and 2023, the Fed's actions have sparked widespread debate among economists, policymakers, and the public. This article delves into the intricacies of federal reserve interest rates, exploring their history, impact, and future outlook to help you make informed financial decisions.
Understanding federal reserve interest rates isn't just for economists or Wall Street analysts. These rates affect everyday life, influencing everything from credit card interest to savings account yields. Whether you're planning to buy a home, invest in the stock market, or save for retirement, keeping an eye on the Fed's monetary policy can provide valuable insights. In the following sections, we'll break down the key aspects of federal reserve interest rates, address common questions, and offer practical advice to help you stay ahead in an ever-changing financial world.
Read also:The Pink Stuff Night Wear Your Guide To Comfort And Style
Table of Contents
- What Are Federal Reserve Interest Rates?
- How Do Federal Reserve Interest Rates Affect the Economy?
- Why Does the Fed Change Interest Rates?
- The History of Federal Reserve Interest Rates
- What Are the Current Federal Reserve Interest Rates?
- How Can You Prepare for Interest Rate Changes?
- What Are the Pros and Cons of High Interest Rates?
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Federal Reserve Interest Rates?
Federal reserve interest rates refer to the benchmark rates set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), a key body within the Federal Reserve System. These rates serve as a guide for financial institutions when they borrow and lend money. Specifically, the federal funds rate—the interest rate at which banks lend to each other overnight—is the most closely watched metric. It acts as a foundation for other interest rates, such as those on loans, credit cards, and savings accounts.
The Fed uses these rates as a tool to manage economic conditions. For instance, lowering federal reserve interest rates encourages borrowing and spending, which can stimulate economic growth. Conversely, raising rates discourages borrowing and spending, helping to curb inflation. This mechanism allows the Fed to influence the economy without direct intervention in markets. Understanding how these rates work is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the financial landscape effectively.
To further clarify, federal reserve interest rates are not directly set for consumers. Instead, they influence the rates that banks and financial institutions charge their customers. For example, when the Fed lowers rates, mortgage rates and auto loan rates may decrease, making it cheaper for consumers to borrow. Similarly, when rates rise, savings accounts and certificates of deposit (CDs) may offer higher yields, benefiting savers. This interconnected system highlights the far-reaching impact of federal reserve interest rates.
How Do Federal Reserve Interest Rates Affect the Economy?
The impact of federal reserve interest rates on the economy is both direct and indirect. When the Fed lowers rates, it makes borrowing cheaper for businesses and consumers. This can lead to increased spending on goods and services, higher investment in business expansion, and a boost in hiring. Lower rates also make it easier for individuals to purchase homes, cars, and other big-ticket items, further fueling economic activity.
Effects on Businesses
For businesses, federal reserve interest rates play a critical role in determining the cost of capital. Lower rates mean cheaper loans, enabling companies to invest in new projects, hire more employees, and expand operations. On the other hand, higher rates can increase borrowing costs, potentially leading to reduced investment and slower growth. This is particularly important for small businesses, which often rely on loans to fund their operations.
Impact on Consumers
Consumers also feel the effects of federal reserve interest rates in their daily lives. For instance, lower rates can reduce the cost of credit card debt and personal loans, making it easier to manage expenses. However, higher rates can increase the cost of borrowing, leading to tighter budgets for households. Additionally, savers benefit from higher rates, as banks typically offer better returns on savings accounts and CDs when the Fed raises rates.
Read also:Demystifying The Simple Succubus Myths Origins And Impact
Effects on Global Markets
Federal reserve interest rates also have a ripple effect on global markets. When the Fed raises rates, it often leads to a stronger U.S. dollar, as higher returns attract foreign investors. This can impact international trade, as a stronger dollar makes U.S. exports more expensive and imports cheaper. Conversely, lower rates can weaken the dollar, potentially boosting exports but increasing the cost of imported goods.
Why Does the Fed Change Interest Rates?
The Federal Reserve adjusts interest rates to achieve its dual mandate: promoting maximum employment and maintaining stable prices. These changes are not arbitrary but are based on a careful analysis of economic indicators, such as inflation, unemployment, and GDP growth. By raising or lowering federal reserve interest rates, the Fed aims to strike a balance between economic growth and price stability.
What Happens When the Fed Raises Rates?
When the Fed raises federal reserve interest rates, it typically does so to combat inflation. Higher rates make borrowing more expensive, which can reduce consumer spending and business investment. This slowdown in economic activity helps to bring inflation under control. For example, during periods of rapid price increases, the Fed may raise rates to cool down the economy and prevent overheating.
What Happens When the Fed Lowers Rates?
Conversely, the Fed lowers federal reserve interest rates to stimulate economic growth. Lower rates make borrowing cheaper, encouraging businesses to invest and consumers to spend. This can help boost employment and GDP growth, particularly during economic downturns. For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic, the Fed slashed rates to near zero to support the economy.
How Does the Fed Decide on Rate Changes?
The decision to change federal reserve interest rates is made by the FOMC, which meets eight times a year. During these meetings, committee members review economic data, assess risks to the economy, and vote on whether to raise, lower, or maintain rates. The Fed's decisions are guided by its long-term goals and are communicated to the public through press releases and statements, ensuring transparency and predictability.
The History of Federal Reserve Interest Rates
The history of federal reserve interest rates is a fascinating journey through economic booms, busts, and recoveries. Over the decades, the Fed has adjusted rates in response to various challenges, from the Great Depression to the 2008 financial crisis. These historical trends provide valuable insights into how the Fed has used interest rates to navigate economic cycles.
For example, during the 1970s, the U.S. faced runaway inflation, prompting the Fed to raise rates significantly under Chairman Paul Volcker. This aggressive approach helped bring inflation under control but also led to a severe recession. In contrast, the early 2000s saw relatively low rates, as the Fed sought to stimulate growth following the dot-com bubble burst and the 9/11 attacks.
More recently, the Fed's response to the COVID-19 pandemic marked a historic shift. In March 2020, the Fed slashed rates to near zero and implemented unprecedented monetary policies to support the economy. As the recovery gained momentum, inflation surged, prompting the Fed to raise rates aggressively in 2022 and 2023. This historical context underscores the Fed's evolving role in shaping economic outcomes.
What Are the Current Federal Reserve Interest Rates?
As of 2023, federal reserve interest rates have been on an upward trajectory, reflecting the Fed's efforts to combat inflation. The federal funds rate currently stands at a range of 5.25% to 5.50%, the highest level in over two decades. This series of rate hikes began in March 2022, as inflation reached levels not seen since the early 1980s.
The Fed's decisions have been closely watched by investors, businesses, and consumers alike. While higher rates have helped to slow inflation, they have also raised concerns about the potential for a recession. The central bank has signaled that it may pause further rate hikes if economic conditions stabilize, but the path forward remains uncertain.
For consumers, the current federal reserve interest rates mean higher borrowing costs but also better returns on savings. Mortgage rates, for example, have risen significantly, making homeownership more expensive. On the flip side, savers are benefiting from higher yields on savings accounts and CDs. These trends highlight the dual impact of federal reserve interest rates on the economy.
How Can You Prepare for Interest Rate Changes?
Preparing for changes in federal reserve interest rates requires a proactive approach. Whether you're a borrower, saver, or investor, understanding how these rates affect your financial situation can help you make informed decisions. Here are some practical tips to consider:
- For Borrowers: If you're planning to take out a loan, such as a mortgage or auto loan, consider locking in a fixed rate before rates rise further. This can save you money over the long term.
- For Savers: Take advantage of higher interest rates by exploring high-yield savings accounts or CDs. These products can help you grow your savings more effectively.
- For Investors: Diversify your portfolio to mitigate the impact of rate changes. Bonds, for example, may underperform when rates rise, so consider allocating more to stocks or other asset classes.
Additionally, staying informed about the Fed's decisions and economic trends can help you anticipate rate changes. Following reliable financial news sources and consulting with a financial advisor can provide valuable insights and guidance.
What Are the Pros and Cons of High Interest Rates?
High federal reserve interest rates have both advantages and disadvantages, depending on your financial situation. Understanding these trade-offs can help you navigate the economic landscape more effectively.
Pros of High Interest Rates
- Higher Savings Yields: Savers benefit from better returns on savings accounts, CDs, and other interest-bearing accounts.
- Lower Inflation: Higher rates can help bring inflation under control, stabilizing prices and preserving purchasing power.
- Stronger Dollar: A higher federal funds rate often leads to a stronger U.S. dollar, which can reduce the cost of imported goods.
Cons of High Interest Rates
- Increased Borrowing Costs: Loans, mortgages, and credit card debt become more expensive, making it harder for consumers and businesses to borrow.
- Slower Economic Growth: Higher rates can reduce consumer spending and business investment, potentially leading to slower GDP growth.
- Risk of Recession: Aggressive rate hikes can increase the risk of a recession, as economic activity slows down.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Federal Reserve Interest Rates?
Federal reserve interest rates are benchmark rates set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) to guide borrowing and lending in the economy. These rates influence everything from consumer loans to business investments.